Common Spatial Pattern
Published:
Introduction of Common Spatial Pattern(CSP) Algorithm
The Common Spatial Pattern (CSP) is a spatial filtering algorithm widely employed in the Brain-Computer Interface (BCI) domain, serving as a benchmark for EEG classification, particularly in motor imagory paradigms.
In this exploration, we embark on elucidating the purpose of the CSP algorithm and its connection between the mathematical concepts and neuroscience. This blog draws from the seminal paper by Ramoser et al. (2000)
The general idea of CSP and the explanation of the name of the algorithm
The purpose of CSP Algorithm is to craft a linear transform, which can also be called as a pair of spatial filters, that maps the original data into a new space with more discriminative features.
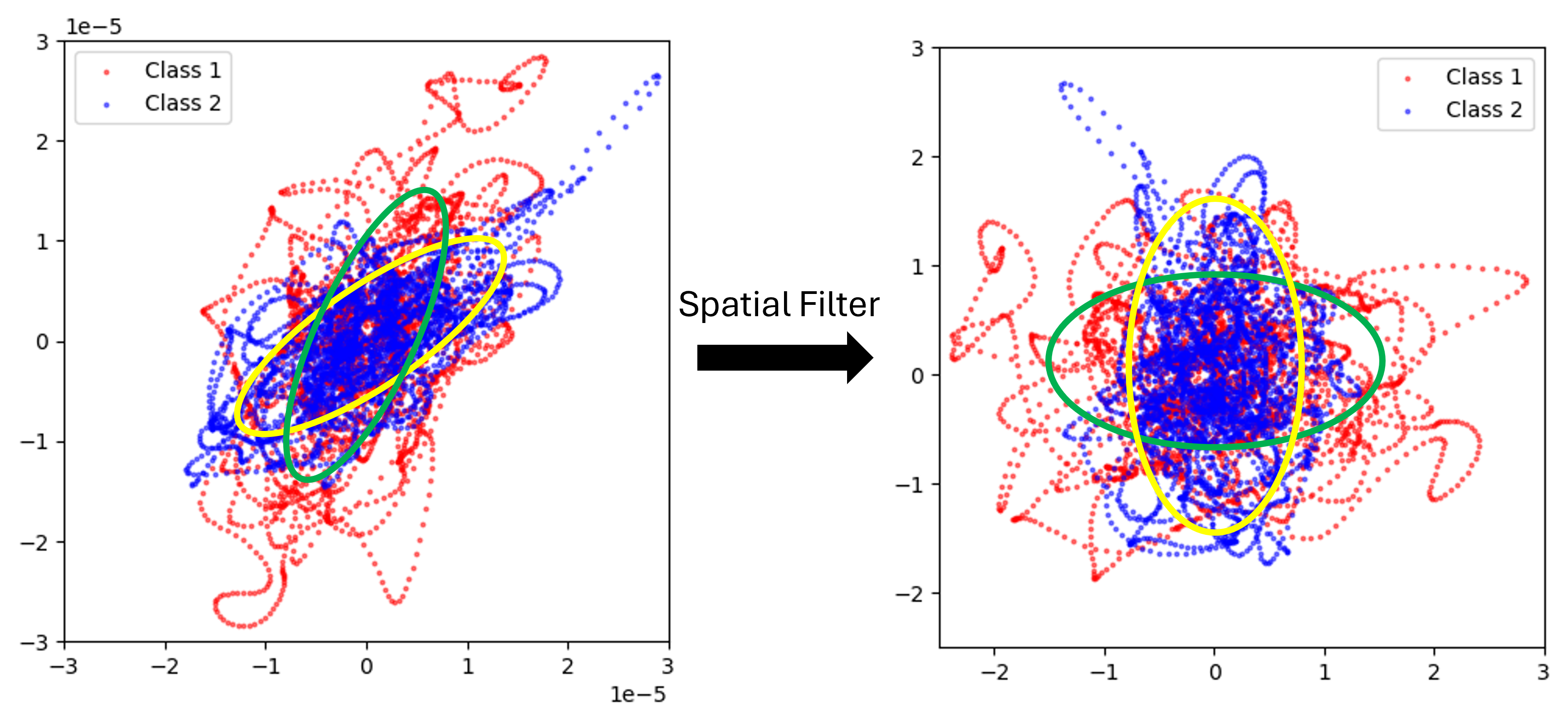
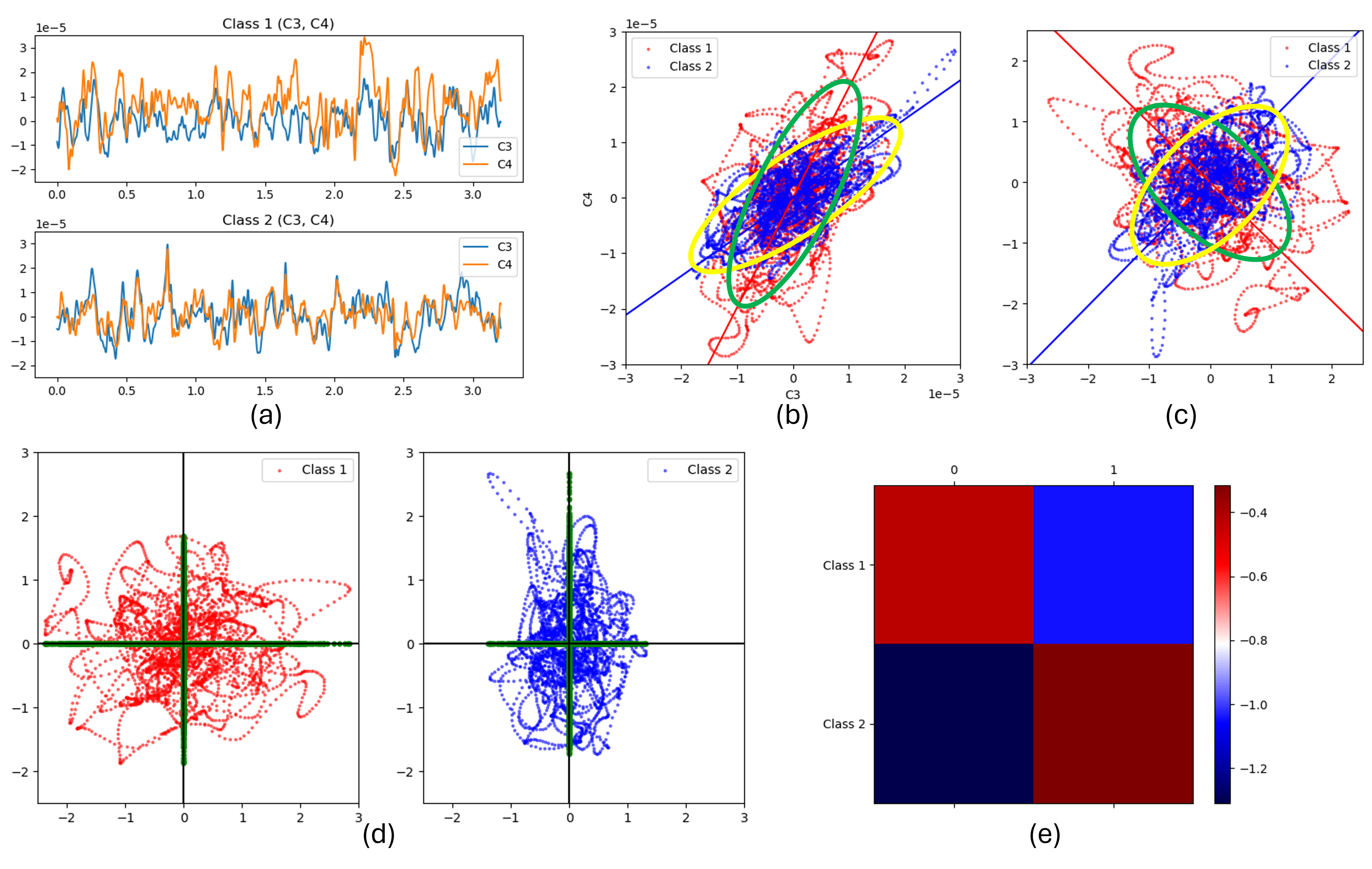
To briefly illustrate with the example below, consider two trials of EEG signals from two distinct classes (Class 1 and Class 2). Focusing on two channels (C3 and C4) for visual reference. Figure (a) displays the EEG signal in the time domain, while Figure (b) presents a scatter plot of C3 and C4. The CSP process involves scretching and rotating the signal distribution using the pair of spatial filters for both classes, as depicted from Figure (b) to (c), where the variance of transformed signal through the former half of the filters is maximized for one class while minimized for the other, while the latter half of the filters exhibit the opposite effect. Subsequently, the distribution is further rotated (from (c) to (d)) and the data is projected into lower-dimensional features for classification (from (d) to (e))
knowledge background of CSP
Before going into the details of CSP, it is essential to grasp some fundamental concepts in linear algebra. If you are not already fimilar with these terms (much like myself), I highly recommend investing some time in learning about them. This foundational knowledge is crucial for a deeper understanding of the algorithm, rather than merely using it.
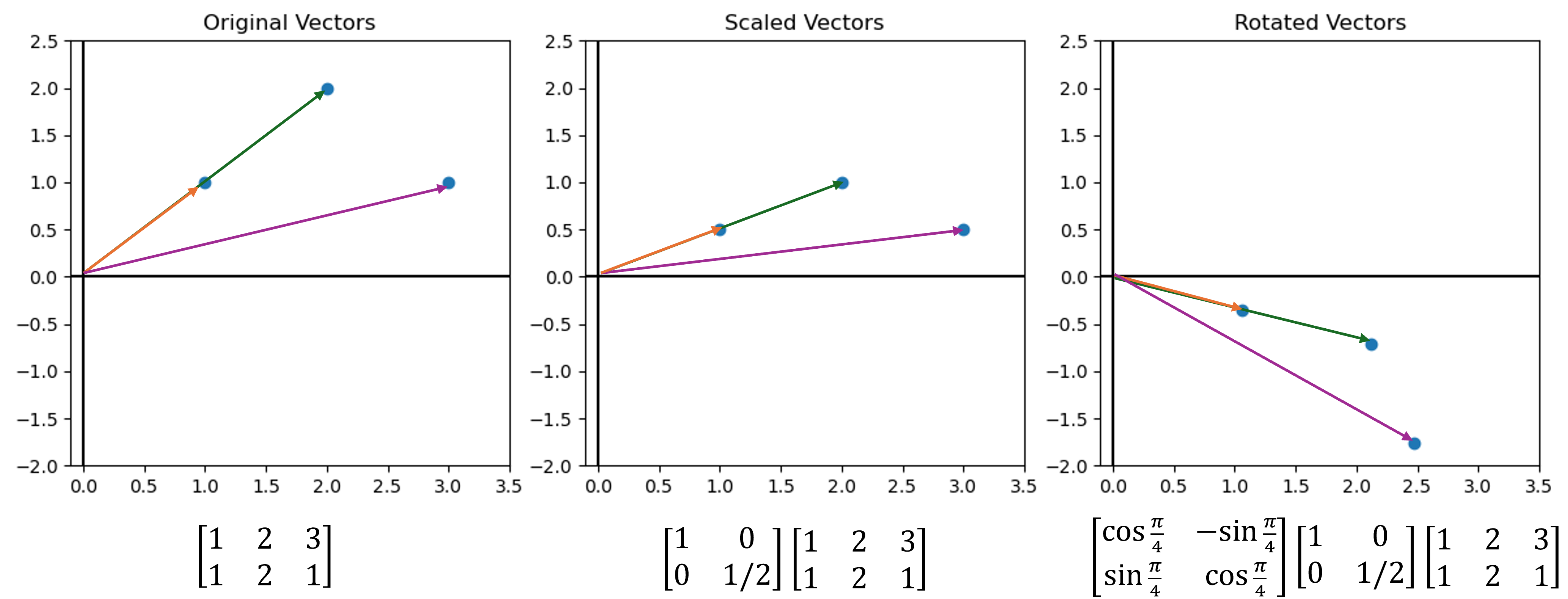
Linear transformations and its relationship with matrix
Linear transformations are mathematical operations that can stretch, rotate, or otherwise alter data points within a vector space while maintaining the integrity of lines and the origin. Through matrix multipulication, these transformations allow data points to be repositioned into a new coordinate system while preserving the fundational structure of the vector space.